If the CFO came to your May board with a forecast that the credit union’s retained earnings margin would fall by 50% in the first six months of this year, it would get your attention.
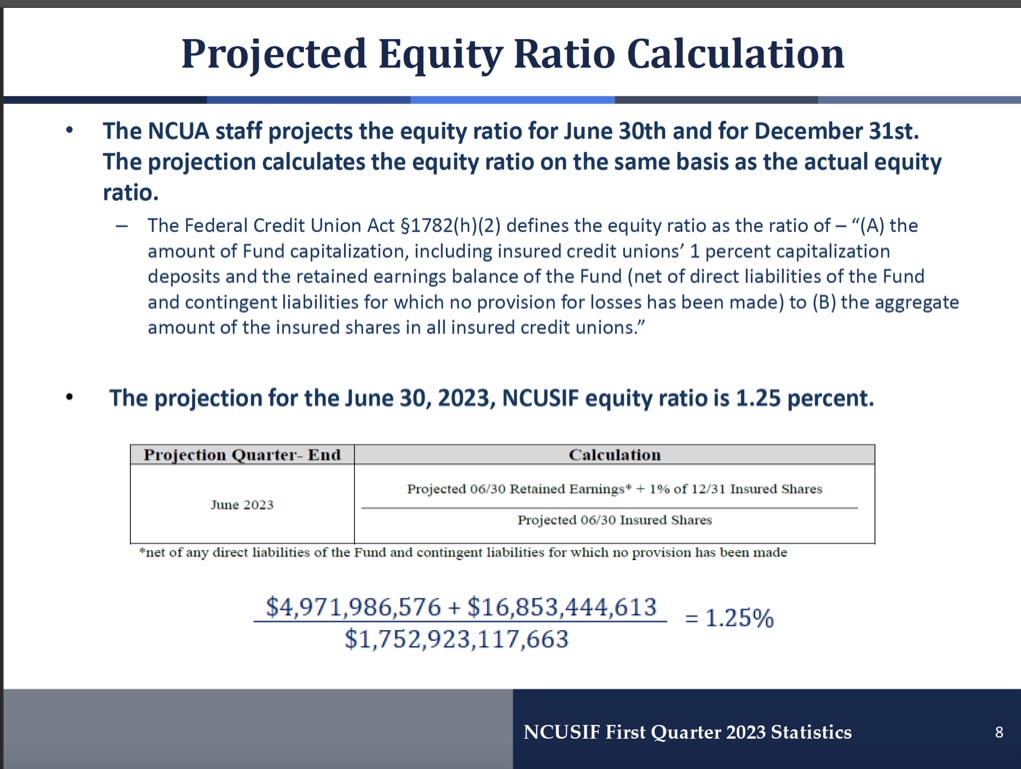
That is what CFO Schied presented in the slide below showing a decline in the NOL from December’s 1.3% to 1.25% by the end of this June. That would be halfway to the 1.20 NOL floor at which the NCUA must come up with a restoration plan.
As summarized in my earlier report, all of the actual credit union CAMELS data, the NCUSIF financial position and other accompanying information was good news. Especially in the context of the first quarter banking failures and the continuing risk in interest rates.
Board members acknowledged the actual resilience of the cooperative system but then picked up the forecasted alarm.
Chairman Harper suggested the actual data was just “the calm before the storm.”
Vice Chair Hauptman opened his comments stating his objective was to protect “the taxpayers” from NCUSIF failure.
Only board member Hood attempted to get behind the numbers. He asked how the $12 million loss reserves expense was determined and the status of proper presentation of the 1% true up. The answers were a polite stonewall.
Similar to a credit union’s net worth, the NCUSIF’s reserve ratio is an easy shorthand for its financial position. The calculation is straight forward. The ratio is simply retained earnings divided by the insured shares at the same date.
This ratio was 29.1 basis points or .291% of insured shares at December 2022. As of March 2023 the ratio was 28.8 basis points. This .3 of one basis point minimal decline in the first 90 days is a far cry from the 5 basis points projected above.
The projected ratio in slide 8 is a made-up number. Its relevance depends on the assumptions used. The estimated growth of insured shares to $1.75 trillion is a 7.2% twelve month increase from 2022. The actual rate of increase as of March 2023 from the year earlier was 2.2%.
The addition to retained earnings for the quarter ending June is just $6 million versus a net income of $41.7 million in the NCUSIF’s just reported March quarter.
The final number in the numerator is the 1% deposit. The calculation above reverts back to the six-month-old December 31, 2022 total deposits. By using this out-of-date number this invented ratio understates the actual 1% deposit total due from credit unions. Including this six-month-old deposit liability misstates the actual ratio and cash due.
The slide’s 1.25% manufactured outcome became the lead in several press reports. It misinforms about the trend in the NCUSIF’s financial position. The ratio’s assumptions were not explained even though they were significantly different from actual trends through March.
Monitoring an accurate Fund equity ratio matters.
Per stature, the actual NOL is calculated at yearend to determine whether a dividend must be paid should the fund’s reserves exceed the NOL cap. The number is also the floor from which a potential premium could be assessed to increase the NOL to a maximum of 1.3% of insured shares. Getting this NOL right is vital for every credit union.
More critically the use of a number from an earlier accounting period to compare with a current period’s insured risk total does not align with standard GAAP accounting practice.
Two Accounting Examples
There are direct accounting precedents with GAAP for how the 1% true up should be reported. They show that the concurrent presentation of insured risk and the legally required true up of the capital deposit base is standard industry practice.
The first example is Deloitt & Touche’s audit of ASI’s required deposit an identical structure to the NCUSIF. From the December 2022 ASI audited financials:
In our opinion, the accompanying financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of
December 31, 2022 and 2021, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the years then ended in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Deloitte & Touche, LLP April 11, 2023
And regarding the deposit requirement:
Participants’ capital contributions that are receivable or payable as of December 31, 2022 and 2021, are presented on a gross basis in the accompanying consolidated financial statements. Included in participants’ equity at December 31, 2022, is a receivable for capital contributions of Primary-insureds of $2,530,000 (no payable). The receivable and payable balances result from annual growth or shrinkage in participating credit union shares and the receivables were substantially collected subsequent to December 31, 2022.
Included in participants’ equity at December31, 2021, is a receivable for net capital contributions of Primary-insureds of $25,200,000. The receivable and payable balances result from annual growth or shrinkage in participating credit union shares and the receivables were substantially collected subsequent to December 31, 2021. (page 13, Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements)
The second example is the recognition in the NCUA’s Operating Fund of an “account receivable,” on the balance sheet and the income statement in its monthly statements postings.
From the January 30, 2023 NCUA Operating Funds monthly financial statements:
The cash position is considered sufficient to cover current and future budgetary obligations of the Fund through April 2023, at which time the Fund will collect the 2023 operating fees from its credit union members. . . Operating fee revenue reflects one twelfth of the 2023 Operating Fees.
A longer explanation of this accounting presentation for the expense receivable in the January 2022 statement:
Other accounts receivable, net had a month-end balance of approximately $10.5 million. Its balance increased by approximately $10.2 million from prior month primarily due to the unbilled receivable for the 2022 Operating Fee. The Operating Fee will be invoiced in March and collected in April.
In other words the Operating Fund recognizes a net receivable and records one twelfth of the total operating fee as income each month even though the fee is not invoiced till March and collected in April.
In these instances the amounts legally due are presented as receivables in ASI and NCUA’s respective audited financial statements and monthly financial presentations.
The 1% True Up Topic Raised Again
Board member Hood asked again about the status of the external assessment of accounting options the NCUA board requested in 2021. CFO’s Schied characterized this external memo saying: “Each option was “non-optimal.” An unusual accounting conclusion.
NCUA has refused to publicly release this expert review under FOIA. What options were reviewed, what data or precedents referenced, and how were the pros and cons presented?
The current practice leads users of the information astray. It potentially shortchanges credit unions’ dividends. NCUA self-interest is keeping the status quo. The memo should be published for all to evaluate.
The credibility of NCA’s oversight of the insurance fund is a function of the legitimacy of the numbers and explanations it provides. If NCUA is not able to present the Fund’s position accurately, at a minimum it leads to misleading conversations.
How an Inaccurate Number Distorts Discussion
The fabricated 1.25 NOL ratio forecast as of the end of next month led to several illusory discussions and unfortunate public headlines.
One board member commented how the Fund’s “margin was narrowing” before “taxpayers will have to pay.” That unfortunate characterization shows the importance of knowing real numbers. In the first 90 days of 2023 the ratio had changed by just .03 of one basis point.
Moreover the only “taxpayers” who are legally bound to support the NCUSIF are members of credit unions. Each sends 1 cent of every savings dollar in their credit union’s 1% deposit in the Fund.
The board member’s observation that “there is not a lot of room between 1.2 to 1.3 equity” unfortunately mischaracterizes the fund’s actual operating performance since 1984. The long term insured loss rate for the fund is just over 1 basis point. Even in the 2008-2010 the net cash losses from natural person credit unions were 3.5, 2.0 and 3.0 basis points of insured shares. The highest cash losses in the three years was $228 million, nowhere close to the “billions” response in the meeting.
In the most recent four years (2019- 2022) which includes the Covid crisis, the economy’s total shutdown and a rising rate cycle, the highest loss from “old school failures” was .3 of one basis point. In 2021 the Fund reported actual net cash recoveries.
An accurate presentation of past and current NCUSIF performance is important in understanding the unique design and resilience of the NCUSIF. Because of this collaborative resource, the credit union cooperative system is much more stable than FDIC insured bank premiums.
The Fund’s relative size to insured risks remains stable in all circumstances. The 10 basis point guardrails (the 1.20-1.30 operating ratio range) today equates to almost $1.8 billion. For comparison, the NCUSIF’s entire total insured losses from 2008 through 2022 were $1.9 billion. The operating expenses in this same period were over $2.4 billion.
The legislative guardrails were put in for a reason. Credit unions feared that open ended funding would just lead to unchecked spending by NCUA. This is what has occurred through increasing the Overhead Transfer Rate allocation to shore up the agency’s ever increasing budgets.
Constantly rising expenses, not insured losses, are the Fund’s largest drain on reserves.
Everyone Can Project NCUSIF Yearend Outcome
Forecasting the NCUSIF’s yearend NOL ratio is simple. Here is the link to a spreadsheet anyone can use. If any difficulty using, please email.
The inputs are portfolio yield, share growth, NCUSIF net income, insured loss and whatever assumptions a user believes are consistent with present trends. The current numbers include the latest actual NCUSIF updates through March 2023. It projects a yearend NOL of 1.2917.
Tomorrow I will review one other slide that is vital to understanding the Fund’s management.






