Do some credit union leaders, the general press and those charged with overseeing the public good believe the member-owners of cooperatives are idiots? I believe those that think and act that way will soon be standing in front of a revolution if the behavior in mergers and other acquisitions continues as described below.
In the first decade of this century a punk rock group, Green Day, wrote a political protest song called American Idiot. The song was a loud screed against the fear and xenophobia which they believed the public media promoted after the Bush administration’s invasion of Irag.
The chorus of this complaint is:
Welcome to a new kind of tension
All across the alienation
Where everything isn’t meant to be okay
In television dreams of tomorrow
We’re not the ones who’re meant to follow
For that’s enough to argue
Abraham Lincoln was gentler when he said, ‘You can fool all people some of the time and some people all the time. But you can never fool all people all the time.”
Today a few hundred of the 4,700 credit unions are led by persons testing Lincoln’s assertion that you can’t fool all the people all the time. Just insert the word member for people.
The ongoing spectacle of credit unions eating their own with the enablers stuffing their pockets to carry out this cooperative cannibalism continues. The examples are piling up. This continued mutual destruction could end up destroying the whole cooperative enterprise. The latest example is the merger of 121 Financial CU with VyStar both headquartered in Jacksonville, FL.
The Setup
Some 90 years ago a group of telephone workers put their nickels, dimes, and quarters into a desk drawer to organize a credit union. It was 1935, the middle of the Great Depression. Over the years this telco-based group effort grew and grew. As it became too large for self-management, the board hired full time professional staff to continue the purpose of building a “home-grown” cooperative serving the greater Jacksonville community.
At December 2023 this nickels and dimes startup had reached $710 million in assets, serving 50,000 members. Its financial performance was strong, continuing to grow loans at 11% and achieving a net worth of 9.05% or well capitalized. Delinquency had ticked up a bit to .64%, but the loss reserve was 140% of all past due loans.
However in November 2023, the current board and senior management decided to end this nine-decade record of member-centered community service.
As reported by CU Today in November 2023, “the credit union told members the merger will provide enhanced services, meet the evolving needs of members and employees, and make a “profound positive impact on its communities.”
It did not identify what those enhanced services would be . . .
In addition, 121 Financial . . .said the merger will further its mission to “Do Good.”
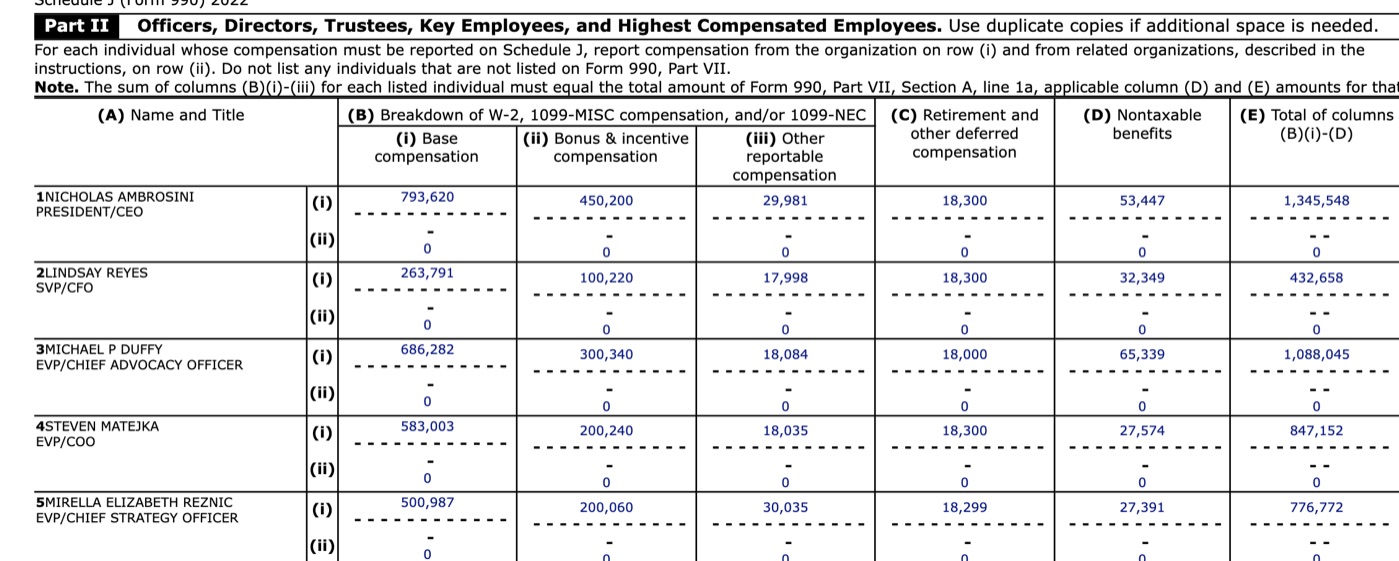
The “doing good” that was disclosed were payouts to the five senior managers of over $900,000 for additional bonuses and salaries detailed at the end of this blog.
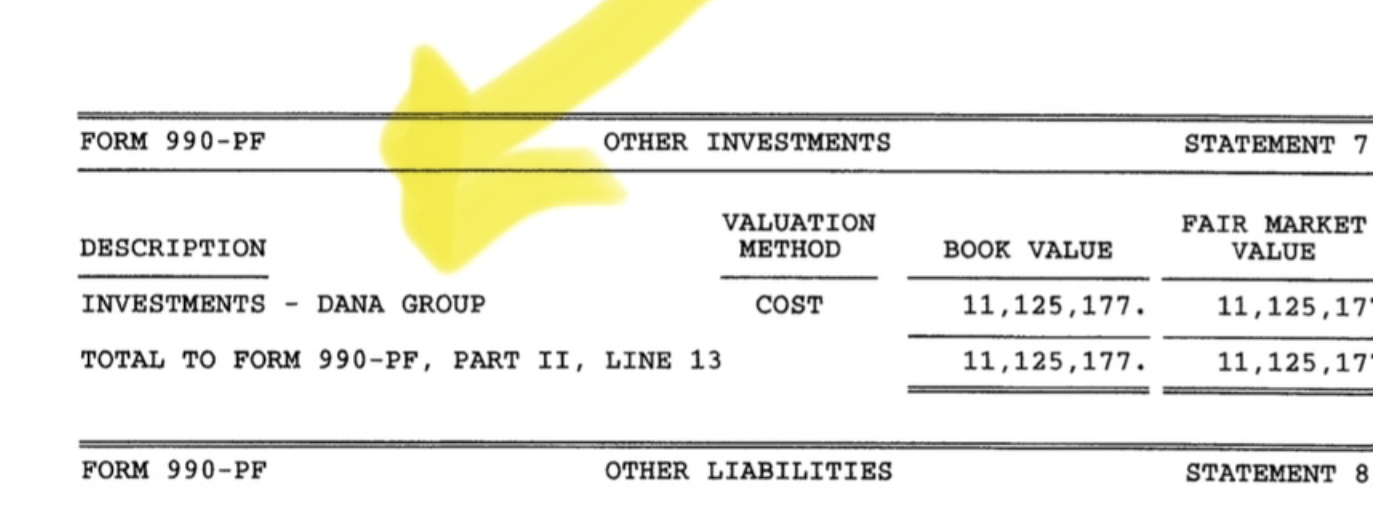
The 50,000 members who had built and owned the credit union received nothing. Just vague promises in return for giving away their $485 million in loans, $177 million in investments, all $25 million in fixed assets, and $63 million in equity, for free.
Who wouldn’t want such a deal? A successful nine decade long ongoing business with a local reputation and loyalty, not sold, but handed over to a local competitor. And the former member-owners get a new set of leaders who have nothing to do with their history or success.
One can understand why 121 Financial’s senior management wants to ensure their future. The recipient of this largesse, VyStar, has 925,000 members, 91 branches and 2,300 employees. It doesn’t need another CEO (whatever the former CEO’s new title-legacy ambassador?) COO, CFO, Sr Lending officer, let alone another Executive Assistant. Their additional compensation was stated as over $900,000 and that does not include significant other benefits in written form from benefit plan terminations and new SERPS.
The leaders claimed that they had contacted a number of other credit unions and this was the best deal. Whether true or not (the shopping part) it does suggest that a number of credit unions passed on this freebee and were not willing to pay the grift.
Or perhaps VyStar thought it was worthwhile to eliminate a local competitor which was outperforming them with the traditional credit union strategic advantage of “relationship banking.” Consider how VyStar would have reacted if PenFed took the bait.
The Members Saw Through the Scam Immediately
When the merger was announced the members immediately set up a website Stop the Merge. The purpose was clear: We need you, The Members of 121 FCU, to help us save our Hometown Credit Union.
On the site are a number of articles describing their concerns and urging members to vote to stop this giveaway. Their most pointed critique was on November 21, 2023, Outrageous Bonus for Top Merger Pushers.
Speaking of “Take-Over” in the merger package, it clearly states that all things 121FCU will go away….Name, Branding, etc. and more community engagement…..What that means is that Vystar will use more of the assets and value of 121 FCU to buy naming rights for sports stadiums and silly promotions. I, for one, just need to be able to trust my financial institution…And I think the 2022 Vystar debacle shows we can’t do that, at least with them.
The bottom line is that 121’sleadership team by closing down this cooperative has broken trust with the owners.
The VyStar Connection-It Takes Two to Tango
CEO Brian Wolfburg has enunciated a clear growth strategy for his tenure. The credit union at one point attempted to purchase the $1.6 billion Heritage Southeast Bancorporation (HSBI)with its 22 branch locations across Southeast Georgia, through Savannah and into the Greater Atlanta Metro area. The effort was called off after a 2022 very public failure of a home banking conversion caused a member uproar.
Even though not completed, this example is relevant to see through this merger. One can understand why Wolfburg wants to eliminate this very successful local competitor which is a burr under his saddle.
Mergers of strong independent firms are anti-competitive. In this case 121 Financial has stronger loan performance, long-established member loyalty and a niche nurtured over decades. When offering to buy HSBI, VyStar offered the bank’s owners a price of 1.80 times book equity. It was also a significant premium over the recent stock price, pre-merger announcement.
However the owners of 121 Financial were offered $0. Instead they were asked to give away their total capital to an entity that had nothing to do with its creation.
Treating credit union member-owners as idiots in an economy that promotes private property is a huge political and business mistake. Members would be treated with more respect if they were bank shareholders.
CEO Wolfburg’s expansion efforts at VyStar depend on two growth hormones: renting capital via subordinated debt (currently $200 million) and acquiring other firms’ assets versus organic growth.
Both of these efforts can work for a while, especially when the cost of funds for years as at or near zero. Now the tide is going out, and as Warren Buffet famously quipped, “we can see who is swimming without any trunks.” Organic growth is hard, but it also is more stable and builds a fortress foundation know as goodwill, but not the intangible financial kind.
For a market indicator of VyStar’s performance this past five years, here are two benchmarks:
The credit union’s return on equity has gone from 7.9% in 2019 to 2.6% in 2023, a CAGR decline of -24% per year. In only 2021 did performance near the longterm market average of 11.8%.
Return on assets in the same five years has gone from .68% to .18% or a negative CAGR of -28.%. In none of the five has ROA reached 1%.
In a market traded firm, this five year record would have triggered calls for changes of leadership or strategy.
The $13.6 billion VyStar needs the financial strengths of 121 Financial to shore up its downtrends. This merger helps VyStar and offers nothing 121’s members cannot have from their credit union.
Where is NCUA?
Every challenged CEO’s defense of this rapacious behavior is excused with two points:
- NCUA approved it;
- The Members Voted for it.
I won’t go into the faux-voting process required by NCUA. Rather the failure to see reality is much deeper especially at the board level. Recall that it was staff that presented multiple examples of self-dealing in proposing the merger reg in 2017.
Chairman Harper does not believe in member-owner rights. He sees members as just consumers. He will protect them with a veneer of enhanced compliance exams. Cooperatives are nothing more than another financial option.
Vice Chairman Hauptman is vague on any philosophy, but sometimes will refer to the free market. His inferred stance is that NCUA can’t run credit unions. However in public pronouncements he makes constant reference to the importance of crypto/blockchain innovation and paying attention to fintechs.
This month will test new board member Otsuka’s ability to bring a fresh eye to both internal and external events. Will she fall back on broad policy statements independent of data. That is the traditional pattern of board newcomers. Or might she challenge the status quo?
CU Today reported the merger had been approved. But neither credit union gave the details of the vote-which is unusual in a contested election. A later story said a member wanted to continue to oppose the combination. One has the feeling there is another shoe to drop here—or will this straw just be one more addition to the CAMELS load at VyStar.
End note: The Payoffs to 121 Financial’s Four Senior Managers and an Executive Assistant
As first reported in November 2023 by CU Today the following are the disclosures of reported benefits:
More Than $900,000 Being Paid in Bonuses, Plus Additional Funds in SERPs, Being Paid Out to 5 Executives
A credit union that is paying more than $900,000 in merger-related compensation to five top execs—plus undisclosed amounts in SERPS—is saying it was “very important to highlight that the board of directors conducted a thorough evaluation of multiple credit unions lasting more than a year before selecting VyStar as the ideal merger partner,” 121 Financial told members.
The $709-million credit union told members the merger will provide enhanced services, meet the evolving needs of members and employees, and make a “profound positive impact on its communities.”
It did not identify what those enhanced services would be. . .
In addition, . . .said the merger will further its mission to “Do Good,” 121 Financial added.
Payout to Senior Executives
The merger related compensation each 121 Financial executive will receive is shown in part below:
- CEO David Marovich, who will continue for five years as SVP-Northeast Community President, with a salary increase of $15,000, two retention bonuses of $122,500 each at six and 12 months after the merger; and who will receive a supplemental executive retirement plan that will pay him 40% of his annual salary of year five upon retirement in year six for a period of five years.
- COO Paul Blackstone, who will continue on for five years and be named SVP-special projects with a salary increase of $95,000, two retention bonuses of $126,250 to be paid six and 12 months after the merger; and the establishment of a SERP that will pay him 35% of his annual salary of year five upon retirement in year six for a period of five years.
- CFO Cyndi Koan, who will continue on for three years as SVP-financial special projects and who will be paid retention bonuses of $35,000 six and 12 months after the merger closes.
- SVP-Lending Cathy Hufstetler, who will retire and receive a year’s severance of $273,000, and retention bonuses of $28,000 at six and 12 months after the merger closes.
- Executive Assistant Nichole LeBlanc, who will continue on for five years as senior executive assistant with a salary increase of $5,000 and with retention bonuses of $9,500 at six and 12 months after the merger.