One of the extraordinary advantages of a credit union charter is the choice of either a state or federal license. This choice has been a critical aspect in credit union’s expanding role in the economy and responding to changing market conditions.
So when I recently received a letter from the CEO of Harvard University Employees Credit Union (HUECU) announcing a members’ special meeting to approve a conversion to a federal charter, I was very interested in why the change.
Was this a one-off situation or an indicator of an imbalance in charter choice in Massachusetts?
A Current Study
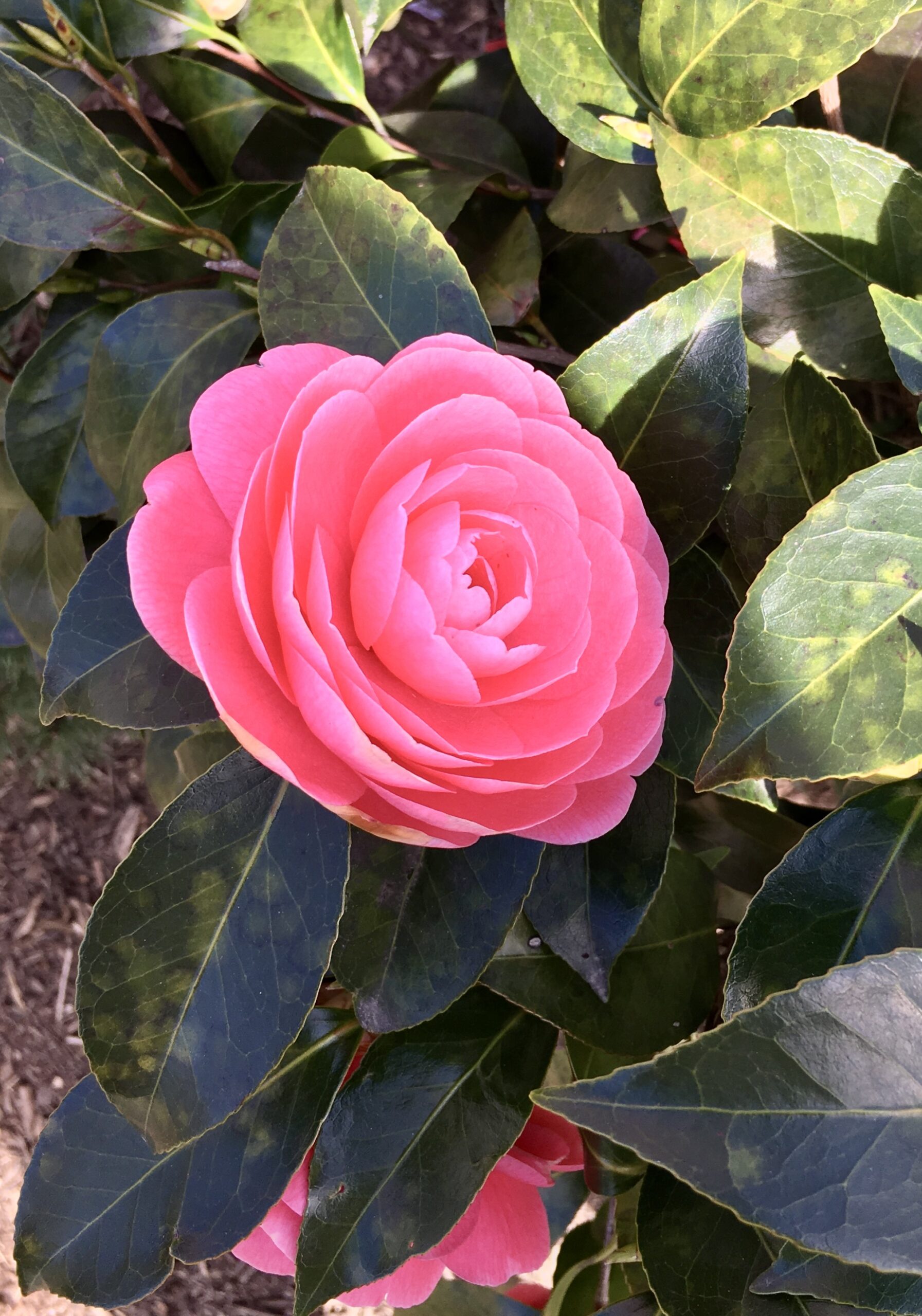
HUECU reported $1.2 billion in assets and loans of almost $1.1 billion, serving 55,000 members at December 2023. Most operating ratios are in a stable to strong range: Net worth 8.5% Delinquency .65%, ROA .28 and operating expenses of 2.74% of average assets.
The loan portfolio continues its healthy growth in three distinct components: an alumni credit card with $44 million in balances, a $252 million student loan portfolio and $721 million real estate loans.
The CEO’s cover letter included five pages summarizing the pros and cons for the action:
Advantages:
- Reduces multiple credit union exam and compliance requirements;
- Potential flexibility with various initiatives, especially branching and CUSO investments;
- MSIC insurance for all deposits above $250,000 will be continued, but is no longer required;
- Easier to open branches outside the state;
- A redefined and broader field of membership with a multiple FCU common bond to seek growth outside Massachusetts:
- No state sales tax, lower supervisory fees, and elimination of state CRA compliance.
Disadvantages:
- The costs of conversion including signage, changes in legal documents, and consultant’s fees totaling as much as $600,000;
- Loss of local regulator accessibility and responsiveness;
- Limited ability to influence national regulation and issues;
- State law offers greater interest rate loan flexibility and longer maturities on other loans.
The special meeting requires a quorum of 18 members and a majority of votes by ballot or in person in favor to approve the conversion.
The CEO’s cover letter states the members will see no operational differences after the conversion.
In addition to my membership in the credit union, the CEO Craig Leonard encouraged members to call in with questions. I was given his email, and we talked for an hour this past Monday.
He outlined three priorities which he hoped to accelerate with this step.
- Faster growth, beyond the Harvard community into other New England states and perhaps Florida;
- Immediately draw in more savings especially as loan demand has always been plentiful—with an initial focus on the small business market;
- Retain the Harvard name (Harvard Federal Credit Union), its strong brand and the relationship of its employees to the University and its benefit plans.
Craig said this topic had been raised several times as he perceived a lack of a “level playing field between state and federal” charters in Massachusetts.
The state is home to approximately 135 credit unions that rank it as the 12th largest in total credit union assets. Of this total, 50 are state charters.
Both regulators have approved the credit union’s business plan forecast. It is now up to the members. Craig holds periodic town hall meetings with members because he believes “I work for you.” This Special meeting is March 26 at the Harvard Faculty Club.
While this may be a unique event, the balance and perceptions of charter advantages are an important metric on the soundness of the credit union system.
Whenever state or federal regulations become less responsive to their credit unions, charter change is a real option for many. It is one means of keeping regulatory accountability. It is also a spur to keep the multiple state regulatory systems, individually much smaller than NCUA. responsive to their local charters.
The State of Dual Chartering
The ability to convert from a state to a federal charter and vice versa remains a uniquely cooperative option.
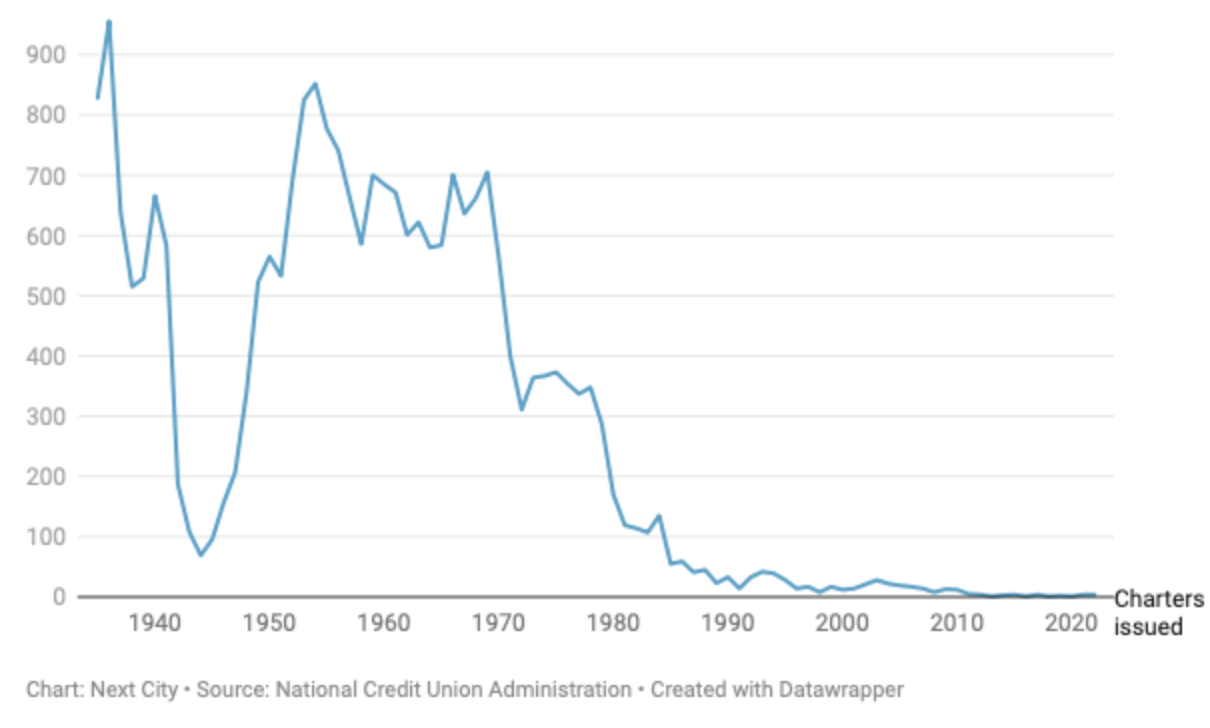
In 2023 there were twelve charter conversions. Nine state credit unions (from seven different states) converted to FCU’s, two federal charters went to state and one state chose ASI insurance versus the NCSIF. The longest serving state charter was Mississippi’s Mutual Credit Union, founded in 1931. Two other Mississippi credit unions also converted to federal.
A choice of share insurance is also permitted in ten states which allow their charters to choose between ASI cooperative insurance or the NCUSIF. This option remains central to a real choice as well as validating the underlying the 1% deposit design of the NCUSIF.
Dual chartering option creates a check and balance, even positive competition, among regulators. It provides an opportunity for a credit union program as some states still do not have a charter option. However, the state system can often change more quickly to meet new market and member needs when response by NCUA may take years or in some situations, never happen.
The dual system is a critical aspect of credit union history. The first credit union charter was in 1909 for St. Mary’s Bank. Until the federal credit union act was passed in 1934, only state charters were available, and then limited to about two thirds of the states.
These state “startups” created multiple charter variations and operating authority. As there was no single example, charter details and oversight were sometimes drawn from already operating financial examples. For example, proxy voting is authorized by nine states, drawn from mutual S&L practice, but not an option for federal charters.
The Turning Point in Dual Chartering: The creation of the NCUSIF
The choice of either a fed or state charter from 1934 onward led to a 30-year period of rapid chartering across America. The states were often the laboratories for change, innovation and system leadership with local leagues and chapters forming potent political state-wide organizations. CUNA itself was an organization of state leagues, not individual credit unions.
The introduction of the NCUSIF in 1970 was led by a group of federal charters in the newly formed direct-member organization NAFCU in the late 1960’s. CUNA opposed this mandatory insurance requirement and supported multiple state-chartered alternatives to the federal program.
CUNA’s fundamental concern was that mandating federal insurance would inevitably create a single regulatory system for all charters. The diversity and choice created by dual chartering would be negated, if not lost all together.
The NCUSIF Override of State Options
This concern that the insurer could become a single regulator had a very quick example. Bob Bianchini, who was simultaneously President of the Rhode Island League and a member of the state legislature, encountered such an issue in the mid 1970’s.
NCUA refused to insure the NOW/checking accounts authorized for Rhode Island state charters. In response, the credit unions formed their own state chartered deposit insurance corporation. In Bob’s words:
The NCUA’s decision refusing to insure Rhode Island credit unions that offered checking account services to its members led to the creation of the private insurer RISDIC .. Seems to me there was never any specific law that would have led to that decision, but rather simply pandering to the commercial banking industry which claimed checking accounts fell strictly under their purview ..
RISDIC would have never gotten off the ground if Rhode Island credit unions that provided checking accounts to its members, could have obtained NCUA insurance.
The other RISDIC insured institutions were Loan & Investment companies. privately owned for profit financial institutions and it was one of those organization’s demise that led to RISDIC’s failure.
NCUA’s insurance power has led to other differences in regulatory interpretations. The insuring requirement has also been a major hurdle for groups seeking new charters.
Ultimately the major advantages of state charters continue to be their more accessible local regulatory oversight and the capacity to respond faster to changing market conditions.
The Final Word
The S&L crisis in the mid 1980’s resulted in that system’s failure of its state sponsored insurance options. It led some credit union leaders to back away from the credit unions’ insurance choice.
In a 1986 speech to the credit union league xecutives (ACULE), former NCUA Chair Ed Callahan, now CEO of Callahan and Associates spoke to the group. He described the importance of choice saying that “the insurer is the regulator.” His words are just as true today. Scroll down to the video.
“The Best Damned System in the Country”