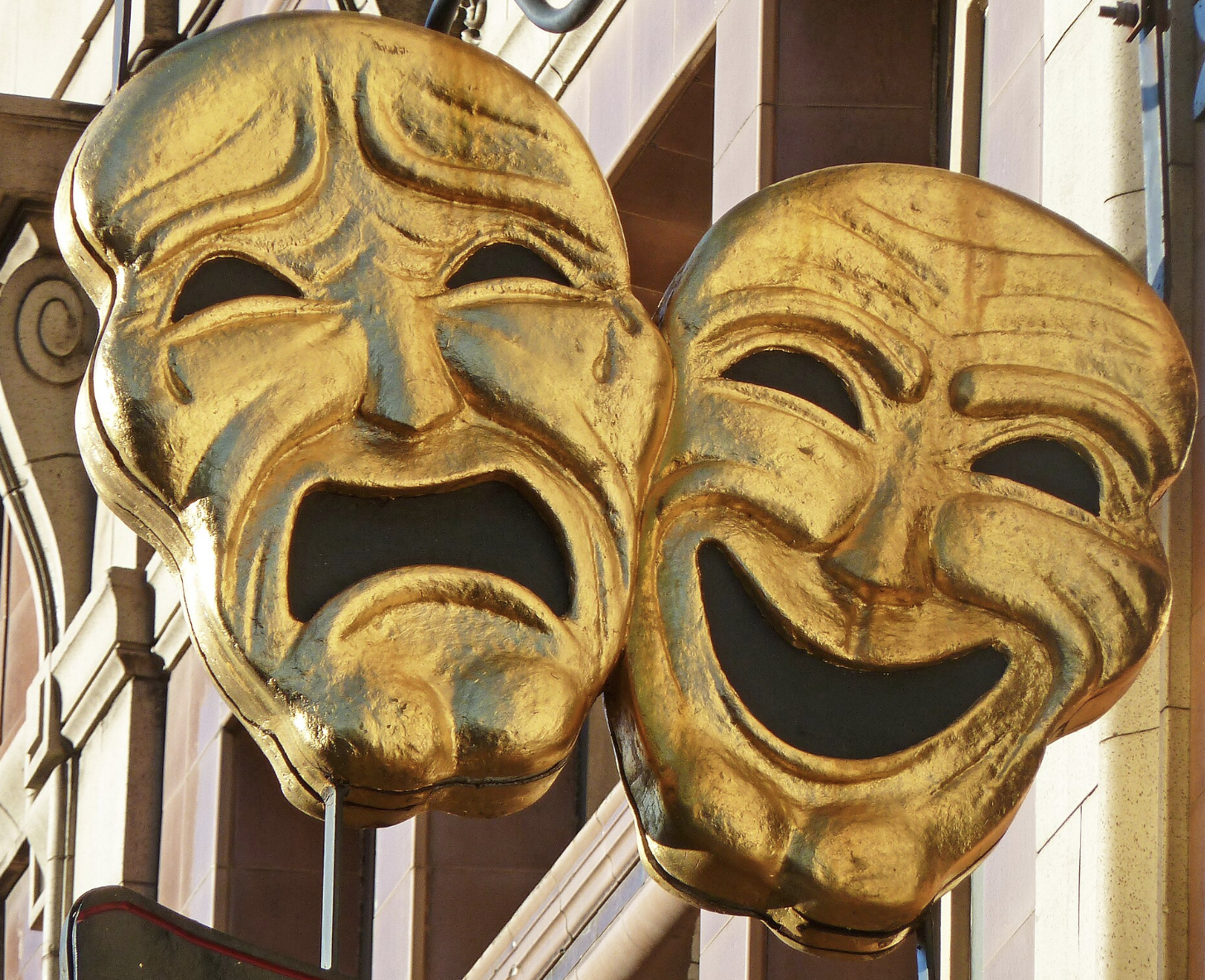
Yesterday I compared credit union’s public personas to the tragedy-comedy masks of ancient Greek theater.
The face I discussed was that of credit union’s institutional achievements: the growing sponsorship of stadiums and sports teams, the continuing mergers of long standing organizations with no member benefit, and the rebranding from legacy origins to aspirational names (Bethpage FCU to FOURLEAF FCU).
Today’s alternate face is member focused. They celebrate the many ways credit unions are sharing and enhancing their value for members and communities.
It is for the reader to decide which credit union expression may be tragic or life affirming.
Sharing the Annual Financial Harvest
The most frequent member-centric announcements this time of year are the numerous bonus dividends credit unions pay members. This is a pattern of member value sharing that goes back decades. Some examples.
The largest yearend bonus in credit union history. That is how the Ogden, Utah Goldenwest Credit Union described its recent $3.5 million bonus dividend. It added, “During the last 21 years, Goldenwest has returned more than $30 million to its members.”
These distribtutions are is not new or unusual. If one types “bonus dividends” into the search box on CU Today’s home page, 2,482 matches are listed. Some stories go back decades of coops sharing success their with member-owners.
These payments can be structured in many creative ways. On December 2, 2024 CEFCU (Peoria, Il) announced a $55 million Extraordinary Dividend: $52.25 million shared equally between borrowers and savers, and $2.75 million going to CEFCU Debit Mastercard users. The video announcement states the credit union has distributed over $500 million in bonus dividends since 2000. Listen to CEO Matt Mamer’s explanation for why and how this bonus was paid. You may view one of many member’s stories featured on the site, that of a single women buying her first home.
The $1.9 billion Tyndall CU paid $1.6 million using the following formula: To get their holiday cash, members had to participate in everyday banking activities, such as online banking, bill pay, direct deposit, card usage, e-statements, and loans. Each member had the opportunity to receive up to $700.
More Than Special Dividends
Being part of a community is more than sharing financial success. It is leaders’ personal participation in special events as described in these LinkIn posts:
From the CEO of Desert Financial: My family and I had the opportunity to volunteer with the Desert Financial team at a special Hometown Heroes event last night at the Phoenix Zoo. The highlight of the night was seeing the kids’ faces light up as they picked out gifts and met Santa. This initiative is a small gesture of gratitude for the sacrifices these veteran and first responder families make for our community and country.
From San Francisco Fire’s CEO: This is my favorite time of year when SF Fire Credit Union staff volunteer alongside members of the San Francisco Fire Department and others to give out toys to children in our local community as part of the annual SFFirefightersToyProgram. Thanks to all who joined us and everyone who supports this amazing program.
Special Community Investments
From the December 11, 2024 Youngstown Business Journal:
YOUNGSTOWN, Ohio – The city has selected 717 Credit Union to administer $13 million in American Rescue Plan Act funds across three programs to improve housing.
As part of the Youngstown Affordable Loan Program, the city allocated $8 million for the construction and/or rehabilitation of quality affordable housing. The credit union proposed to parlay the $8 million into not only funding for housing development, but also $35 million worth of discounted mortgage financing.
To begin development, 717 will create a $5 million revolving commercial development fund to be used for developers to rehabilitate vacant downtown buildings into residential condos, to build homes on vacant lots and to develop neighborhoods. After renovation or construction, the units will be sold to individual buyers and the funds recuperated to be invested in additional projects.
A press release yesterday from SECU North Carolina:
| SECU Foundation Initiates Phase Two Disaster Relief Package of $1.75 Million for Western North Carolina |
RALEIGH, N.C. – SECU Foundation’s Board of Directors approved a phase two disaster relief package with an additional $1.75 million in grants to three organizations, providing intermediate assistance to the hardest hit residents and communities impacted by Hurricane Helene. Funds awarded will help address temporary housing needs, financial crises, and food insecurity. Grantees include:
Phase two funding builds upon the Foundation’s $3.75 million relief package announced in October to help expedite provisions of water, food, supplies, shelter, and other emergency services to Western North Carolina. |
Credit Union Teams Having Fun Supporting their Community
The annual polar plunge with purpose video from Affinity Plus FCU (St. Paul, MN) for the Special Olympics program.
(https://creditunions.com/features/polar-plunge-with-a-purpose/)
A Credit Union’s Example of It’s a Wonderful Life
Every day in numerous communities, credit unions put their members’ well being first in all they do. They are the current expression of George Bailey’s mutual savings and loan in Frank Capra’s memorable film .
Here is one real life example from Wright-Patt Credit Union in Dayton, Ohio:
(https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yMJT0nneRaM&t=18s)
The Credit Union Challenge
Which mask, the corporate or the member facing one, will the American public see in credit unions today?
Will it be the continuing acquisitions fueled by payments to senior leaders, the public branding campaigns and naming rights on buildings, suplemented with continued efforts to purchase banks? Or, wlll member-owners recount stories of goodwill, shared financial success and innovative projects with partners to advance their communities?
If institutional success dominates public discussion and headline events, the results could be tragic for a separate, member-owned cooperative system. Does American really need more growth maximizing financial firms fueled by internal and external acquisitions?
If special member value delivered results are the lead story, America could certainly benefit from these modern day George Bailey-like coops. Ones where purpose for member and community progress are the priority.
I believe it is clear which expression members prefer; but will their leaders meet this moment for their institution’s choice? And the movement’s future?